Overview¶
Hunter¶
| docs | |
|---|---|
| tests | |
| package |      |
Hunter is a flexible code tracing toolkit, not for measuring coverage, but for debugging, logging, inspection and other nefarious purposes. It has a simple Python API and a convenient terminal API (see Environment variable activation).
API is considered unstable until 1.0 is released.
- Free software: BSD license
Installation¶
pip install hunter
Documentation¶
Overview¶
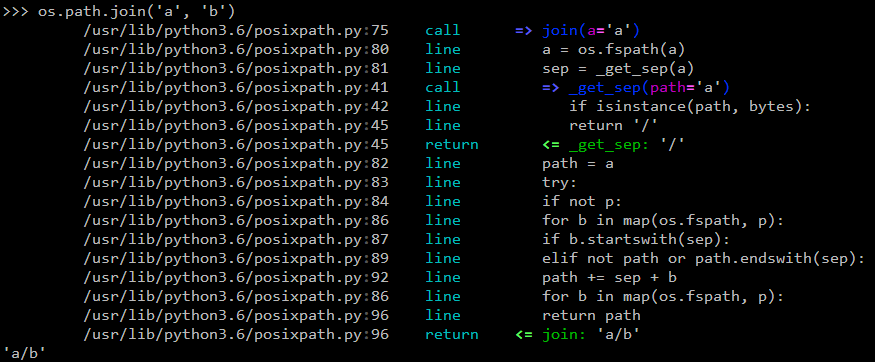
The default action is to just print the code being executed. Example:
import hunter
hunter.trace(module='posixpath')
import os
os.path.join('a', 'b')
Would result in:
python2.7/posixpath.py:60 call def join(a, *p):
python2.7/posixpath.py:64 line path = a
python2.7/posixpath.py:65 line for b in p:
python2.7/posixpath.py:66 line if b.startswith('/'):
python2.7/posixpath.py:68 line elif path == '' or path.endswith('/'):
python2.7/posixpath.py:71 line path += '/' + b
python2.7/posixpath.py:65 line for b in p:
python2.7/posixpath.py:72 line return path
python2.7/posixpath.py:72 return return path
... return value: 'a/b'
- or in a terminal:
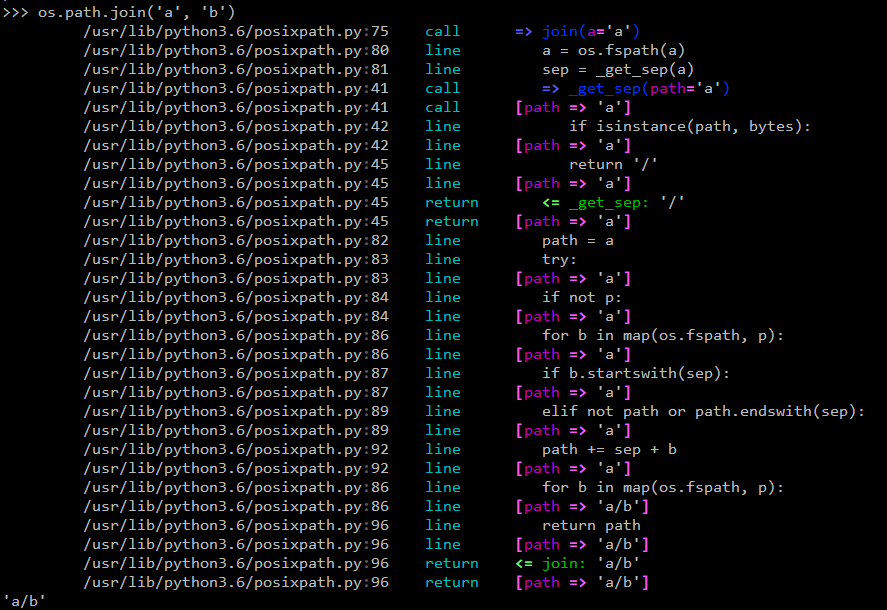
You can have custom actions, like a variable printer - example:
import hunter
hunter.trace(hunter.Q(module='posixpath', action=hunter.VarsPrinter('path')))
import os
os.path.join('a', 'b')
Would result in:
python2.7/posixpath.py:60 call def join(a, *p):
python2.7/posixpath.py:64 line path = a
vars path => 'a'
python2.7/posixpath.py:65 line for b in p:
vars path => 'a'
python2.7/posixpath.py:66 line if b.startswith('/'):
vars path => 'a'
python2.7/posixpath.py:68 line elif path == '' or path.endswith('/'):
vars path => 'a'
python2.7/posixpath.py:71 line path += '/' + b
vars path => 'a/b'
python2.7/posixpath.py:65 line for b in p:
vars path => 'a/b'
python2.7/posixpath.py:72 line return path
vars path => 'a/b'
python2.7/posixpath.py:72 return return path
... return value: 'a/b'
- or in a terminal:
You can give it a tree-like configuration where you can optionally configure specific actions for parts of the tree (like dumping variables or a pdb set_trace):
TODO: More examples.
Environment variable activation¶
For your convenience environment variable activation is available. Just run your app like this:
PYTHONHUNTER="module='os.path'" python yourapp.py
On Windows you’d do something like:
set PYTHONHUNTER=module='os.path'
python yourapp.py
The activation works with a clever .pth file that checks for that env var presence and before your app runs does something like this:
from hunter import *
trace(<whatever-you-had-in-the-PYTHONHUNTER-env-var>)
That also means that it will do activation even if the env var is empty, eg: PYTHONHUNTER="".


